Digitalization Progress
With the introduction of computer systems into judicial affairs, courts have been able to handle various tasks more efficiently. These include case management, registration services, family-relations registration, and court deposit processing. Built upon a nationwide high-speed internet network, the judiciary now provides a wide range of court services to the public, including the Judicial Web Portal, the Comprehensive Legal Information System, case search services, internet-based registry information, court auction information, electronic family relations registration, and electronic deposit. Recently, as the generation and distribution of electronic documents have become more common, driven by advances in IT and the growing public demand for access to judicial information and communication with courts, the judiciary has established an electronic litigation system. This system is supported by robust judicial digital capabilities that meet the public’s rising expectations.

Since 1979, when the Supreme Court first requested the Korea Institute of Science and Technology to conduct a feasibility study on the computerization of judicial affairs, the Court has continuously advanced the digitalization of its operations. In 1986, the Supreme Court initially developed the civil system. This system led to the computerized processing of civil affairs, and in 2002, the Court fully implemented a Case Management System to improve efficiency. Later, in 2007, a customized trial support system called JUSTICE (Judge’s Unified System for Intelligent Case Management) was completed. JUSTICE provides comprehensive support to judges, including assistance with managing trial schedules, tracking case progress, and drafting judgments electronically.
In addition to trial work, the Supreme Court has established a cutting-edge information technology system to digitize court-related registration services, family-relations registrations, and deposits, thereby enhancing the convenience of both internal and external court users.
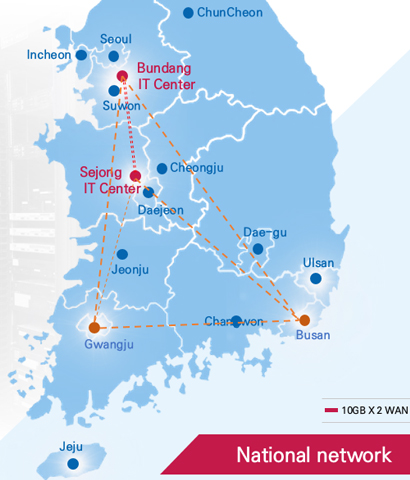
In 2008, the Supreme Court established the Supreme Court IT Center, which serves as the foundational infrastructure for the integrated operation of the judicial information system. Auxiliary data centers were also built in Daejeon, Busan, and Gwangju, ensuring stable 24-hour, 365-day system operation.

In response to the increasing demand for space to house growing information system equipment and to prepare for potential disasters or emergencies such as fires or earthquakes, a separate data center was required to carry out tasks related to registration and family-relations registration, in addition to judicial services. Therefore, the Supreme Court Registry Information Center (Sejong) opened its doors in July 2021 and has been operating smoothly ever since. To ensure continuity of operations and minimize service disruptions in the event of a disaster or emergency at the Supreme Court IT Center in Bundang, all critical data from judicial, registry, and family information systems is continuously replicated in real time between both centers. This backup system allows for data restoration even if either center is damaged.

Court Network System
The judiciary first installed its computer network in 1995 in 28 courts, which accounted for 16.8% of the 166 courts nationwide. In 2004, a dual ultra-speed network system was installed in all courts, where it has been operating ever since. The judicial network uses LAN and inter-networking. All courts, including district and municipal courts, are interconnected via routers, forming a large-scale internet network supported by the Supreme Court IT center (Bundang) and the Supreme Court Registration IT center (Sejong). To maximize network efficiency, external networks, such as those of the Ministry of the Interior and Safety, prosecutors’ offices, and banks, are also connected through dedicated lines.
To ensure robust security, an intrusion detection system and an anti-virus system have been installed. In addition, multiple firewalls and virtual private networks have been in place to enhance security further when external access is required. With the expansion of e-litigation, the volume of electronic data exchanged between internal and external systems has grown. In response, the judiciary is working to expand bandwidth and improve transmission efficiency across its networks. It has also adopted Software-Defined Data Center technology to support a judicial network system with high availability, scalable services, and more efficient maintenance.